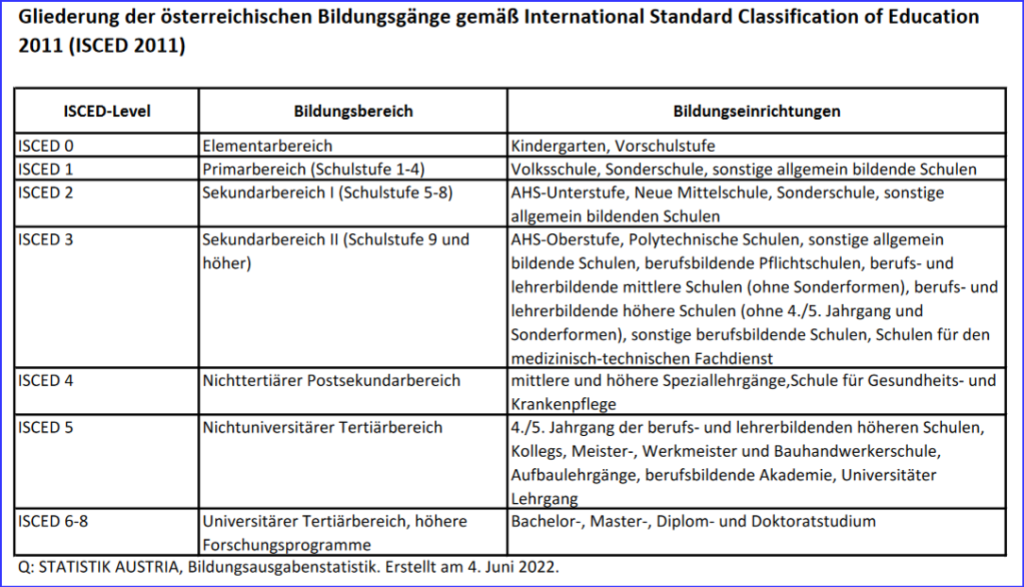
| NADEUMs Vorschlag zur Gliederung des internationalen Bildungssystem | ||
|---|---|---|
| ISCED 0 | Elementargruppen/Bereich | Babykrippen, (0-2) Kindergarten, (3-4) Vorschulstufe (4-6/7) |
| ISCED 1 | Primarbereich /Schulstufe 1-4 | Volksschule (6-10) Sonderschulen (7-10) Private & sonstige Schulen (6-10) |
| ISCED 2 | Sekundarbereich I / Schulstufe 5-8 | AHS-Unterstufe (10-14) Neue Mittelschule (10-14) Spezialschulen aller Art (10-14/15) Medizinischefachschulen: (10-15) Handwerkfachschulen aller Art (10-15) |
| ISCED 3 | Sekundarbereich II / Schulstufe 9 und höher | AHS-Oberstufe (14-18) Polytechnische Schule (14-15) Spezialschulen aller Art (14-18/19) Handwerkfachschulen aller Art (15-20) |
| ISCED 4 | Nichttertiärer Postsekundabereich I | Spezialschulen: Fachhandwerker*Innen: (14-19) Pädagogische Schulen : (14-19) [Babygrippen/Kindergarten/Volksschulen sowie Sonderschulen] Gesundheits- u. Krankenpflegeschulen sowie Medizinisches Fachpersonal: (14-20) |
| ISCED 5 | Nichtuniversitärer Tertiärerbereich II | Berufsschulen f Pädagogen /Lehrer: (19-24) [AHS, Neue Mittelschule, Spezialschulen aller Art] Fachpersonalschulen: (19-24) Meister aller Art (Selbstständige) Aufbaulehrgänge, Universitäre Lehrgänge, Berufsbildende Akademische Lehrgänge, |
| ISCED 6 | Universitärer Pädagogenbereich | Ausbildung von Pädagogen (20-24) |
| ISCED 7 | Universitärer Tertiärbereich | Aller Fachrichtungen (20-24/26/28/30) Bachelor-, Master-, Diplomstudium |
| ISCED 8 | Höhere Forschungs-Programme | Ausbildung aller Art (20-30) Diplom-, Doktorstudium |

Dieser Text wurde 1:1 von der Homepage der UNECSO übernommen:
NADEUM der Initiator von ACAPMUSSC-MYC (sollte in ganz AFRIKA ausgerollt werden) unterstützt diese Forderungen voll und ganz und schlägt der AU vor, sich innerhalb der AU auf einen gemeinsamen Lernstufenplan zu einigen, damit die Absolventinnen und Absolventen und ihre Zertifikate / Zeugnisse in allen Staaten der AU anerkannt werden können und keine Nostrifizierungen nachholen müssen.
This text was taken 1:1 from the UNECSO homepage:
NADEUM the initiator of ACAPMUSSC-MYC (should be rolled out throughout AFRICA) fully supports these demands and proposes to the AU to agree on a common learning level plan within the AU so that graduates and their certificates / diplomas can be recognised in all AU states and do not have to catch up on nostrifications.
| Quelle: Source: About ISCED The world’s education systems vary widely in terms of structure and curricular content. Consequently, it can be difficult to compare national education systems with those of other countries or to benchmark progress towards national and international goals. The International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED 2011) provides a comprehensive framework for organizing education programmes and qualification by applying uniform and internationally agreed definitions to facilitate comparisons of education systems across countries. ISCED is a widely-used a global reference classification for education systems that is maintained and periodically revised by the UIS in consultation with Member States and other international and regional organizations. ISCED 2011 is the second major revision of this classification (initially developed in the 1970s and revised in 1997). It was adopted by the UNESCO General Conference in November 2011. ISCED is essential for collecting and analysing cross-nationally comparable education statistics. The accompanying ISCED Fields of Education and Training 2013 (ISCED-F) classifies education programmes and related qualifications by fields of study according to the broad domain, branch or area of content covered. The ISCED 2011 Operational Manual provides further guidelines for classifying national education programmes and related qualifications according to ISCED 2011. The new addition to the ISCED classifications family, the International Standard Classification of Teacher Training Programmes (ISCED-T 2021), classifies education programmes and the related qualifications by education levels and fields. The UIS works closely with Member States and its data collection partners (such as OECD and Eurostat) to map education systems and collect data according to the ISCED classification. National ISCED mappings are published on our page devoted to ISCED mappings. The UIS has another website to provide data users with information on Education Management Information Systems, which is available here. |
ISCED 2011-Diagramme aller Staaten
1.) Die ISCED-Diagramme aller Staaten, die das UNESCO-Konzept der SDG2030-Weiterbildung und Wissenserweiterung unterzeichnet haben, sind unter diesem Link einzusehen. Dabei ist zu beachten, dass alle Staaten ihr eigenes Schulsystem-Diagramm haben.
Diese Länderdiagramme vermitteln ein visuelles Bild von der Struktur der nationalen Bildungssysteme, die nach ISCED 2011 klassifiziert sind. Die Diagramme basieren auf von den Mitgliedstaaten bereitgestellten Zuordnungen, die intern überprüft und von den Ländern genehmigt wurden. Die wesentlichen Metadaten liefern den Datennutzern spezifischere Informationen zur besseren Interpretation der vom UIS erstellten Bildungsindikatoren, während die Gliederung der Bildungssysteme nach ISCED 2011 eine länderübergreifende Vergleichbarkeit der Daten ermöglicht. Die Länder-ISCED-Diagramme sind nach SDG 4-Regionen geordnet.
1.) Under this link you will find the ISCED diagrams of all countries that have signed the UNESCO concept of SDG2030 Education and Knowledge Enhancement. Please note that all countries have their own school system diagram.
The country diagrams show you at a glance how the national education systems are structured according to ISCED 2011. The diagrams are based on mappings provided by the Member States, reviewed internally and approved by the countries. The essential metadata provides data users with more specific information to better interpret the education indicators produced by the UIS. At the same time, the categorisation of education systems according to ISCED 2011 enables a cross-country comparison of data. The country ISCED diagrams are organised according to SDG 4 regions.
Brunei Darussalam;
Cambodia;
China;
China, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region;
China, Macao Special Administrative Region;
Indonesia;
Lao People’s Democratic Republic;
Malaysia;
Philippines;
Singapore;
Thailand;
Timor-Leste;
Viet Nam



Georgien, Armenien, Azerbaidschan: gehören wohin >EURASIEN
AU – Nord Africa: Algeria;
(Eurasien – ) Armenien;
Aserbaidschan;
Bahrain;
(Levante – ) Cyprus Zypern;
AU – Nord Africa: Egypt;
Georgien Georgia;
Irak Iraq;
(Levante – ) Israel;
(Levante – ) Jordan;
(Mesopotamien – Vorder Asien) Kuwait;
(Levante – ) Libanon Lebanon;
AU – Nord Africa: Libya;
AU – Nord Africa: Morocco;
Oman;
Palästina Palestine;
Katar Qatar;
Saudi Arabien;
AU – Nord Africa: Sudan;
Syrian Arab Republic;
AU – Nord Africa: Tunisia;
Türkiye;
United Arab Emirates;
Yemen;


Albania;
Andorra;
EU-West-Europa:
Austria; Könnte als Beispiel für die AU verwendet werden [EU-Western Europe: Austria; could be used as an example for the AU]
Belarus;
Belgium;
Bermuda;
Bulgaria;
Kanada Canada;
Kroatien Croatia;
Tschechien Czechia;
Dänemark Denmark;
Estland Estonia;
Finnland Finland;
EU-West-Europa: France;


Polen Poland;
Portugal Portugal;
Republik Moldau Republic of Moldova;
Rumänien Romania;
Russische Föderation Russian Federation;
San Marino San Marino;
Slowakei Slovakia;
Slowenien Slovenia;
Spanien Spain;
Schweden Sweden;
Schweiz Switzerland;
Ukraine Ukraine;
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland;
United States of America
Cook Islands;
Kiribati;
Marshall Islands;
Niue;
Palau;
Samoa;
Solomon Islands;
Solomon Islands;
Tuvalu;
Vanuatu;



Equatorial Guinea;
Eritrea;
Eswatini;
AU – East Africa: Ethiopia;
Gabon;
Gambia;
Ghana;
Guinea;
Guinea-Bissau;
AU – East Africa: Kenya;
Lesotho;
Liberia;
Madagascar;
Malawi;

Mali;
Mauritania;
Mauritius;
Mozambique;
Namibia;
Niger;
Nigeria;
Rwanda;
Sao Tome and Principe;
Senegal;
Seychelles;
Sierra Leone;
AU – South Africa: South Africa;
AU – East Africa: South Sudan;
Togo;
Uganda;

AU – East Africa: United Republic of Tanzania;
Zambia;
Zimbabwe;
Wissenswertes kundgetan, Aktualisierung am: 2024-10-02 ; Erstellt am 2024-09-24 Übersetzungen oder Lectorate mit Hilfe von DeepL.com & Write verfasst. <> Translations or lectorates written with the help of DeepL.com & Write.