African Community Action Programme for the Mobility of University Students and Skilled Craftspeople-as-well-as-Migration,Youth-and-Children.
in this part of the project the ending ‘-MYC’ will have meaning

PM (Projekt Manager) Yussif Ismael Makram from „P004 ACAPMUSSC-MYC„
Roles and Responsibilities
1) Developing comprehensive program plans, strategies, and objectives that align with the organization’s mission and objectives.
2) Conducting needs assessments, stakeholder consultations, and situation analyses to inform program design and implementation.
3)activities are executed according to established timelines, budgets, and quality standards.
4) Coordinating with program, volunteers, and community members to facilitate the delivery of program activities and services.
5) Monitoring progress, tracking milestones, and addressing challenges or barriers to program implementation in a timely manner.
6) Managing program budgets, expenditures, and resources to ensure efficient use of funds and compliance with donor requirements and organizational policies.
7) Building and maintaining partnerships with community leaders, local organizations, government agencies, and other stakeholders to leverage resources, expertise, and support for program implementation.
8) Conducting regular reviews, evaluations, and learning sessions to reflect on program achievements, share lessons learned, and adapt strategies based on evidence and feedback.
Our „Project Manager“ within ACAPMUSSC-MYC who will introduce children, youth and young adults to „P004 ACAPMUSSC-MYC (ISCED 1 -4)„; “ is „PM Yussif Ismael Makram“.
Makram Yussif Ismael
Kenya, Turkana county,
Kakuma 3, Zone 1, Block 2
Phone Number: +254702860950
First E-Mail – mailto: kabongomakram@gmail.com
second one : youtamyousifismail@gmail.com
| German | English |
|---|---|
| Unser Projektmanager bei ACAPMUSSC-MYC, der Kinder, Jugendliche und junge Erwachsene in ACAPMUSSC-MYC einführt, ist „PM Yussif Ismael Makram“. Wir werden die Internationale Standardklassifikation des Bildungswesens (ISCED) anwenden, die im OECD-Raum von 34 Ländern anerkannt wird, die dieses vergleichbare Schulsystem anerkennen. Quellenangabe: ISCED | Our project manager within ACAPMUSSC-MYC who will introduce children, youth and young adults to ACAPMUSSC-MYC is ‘PM Yussif Ismael Makram. We will adapt the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED) which is recognised in the OECD area by 34 countries that recognise this comparable school system. Source reference: ISCED |
| Erklärung für | Explanation for |
| 0 til 3 years old | 3 til 6 years old | 6 til 10 years old | 10 til 15 years old | 15 til 20 years old | 20 til 23 years old | 20 til 25 years old | 20 til 28 years old | 20 til 30 years old | 20 so long as you will |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stufe 0 – Elementarbereich Level 0 – elementary area | Stufe 0 – Elementarbereich Level 0 – elementary area | Stufe 1 – Primarbereich Stage 1 – Primary | Stufe 2 – Sekundarbereich I Stage 2 – Secondary Level I | Stufe 3 – Sekundarbereich II Stage 3 – Upper secondary education | Stufe 4 – Post sekundarer, nicht tertiärer Bereich Level 4 – Post secondary, non-tertiary area | Stufe 5 – Kurzes tertiäres Bildungsprogramm Level 5 – Short tertiary education programme | Stufe 6 – Bachelor- bzw. gleichwertiges Bildungsprogramm Level 6 – Bachelor’s or equivalent educational programme | Stufe 7 – Master- bzw. gleichwertiges Bildungsprogramm | Stufe 8 – Promotion bzw. gleichwertiges Bildungsprogramm |
| Kinder-grippe | Kinder-garten, Vor-schule | Grund-wissen | fertiges Grund-wissen | Lehrlinge Fach-hand-werker*Innen, Gesellen*Innen | Ing. / Fach-kräfte | Diplome aller Fach-gebiete | BA. aller Fach-gebiete | MA. aller Fach- gebiete | DR./Mag. aller Fach- gebiete |
| Babys + Mütter | Natur-Kunde I | + Natur-kunde, | Emphatie, Ethik, Umweltschutz | Fach-Handwekliche Berufe | Diplom. Medizinische Berufe | ||||
| Berufs-Schulen, Gesellen | Berufs-Schulen, Meister | ||||||||
Contents
- 1 International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED)
- 1.1 Level 0 – Elementary
- 1.2 Level 1 – Primary education
- 1.3 Level 2 – lower secondary level
- 1.4 Level 3 – Secondary level II
- 1.5 Level 4 – Post-secondary, non-tertiary education
- 1.6 Level 5 – Short tertiary education programme
- 1.7 Level 6 – Bachelor’s or equivalent education programme
- 1.8 Level 7 – Master’s or equivalent educational programme
- 1.9 Level 8 – Doctorate or equivalent educational programme
International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED)
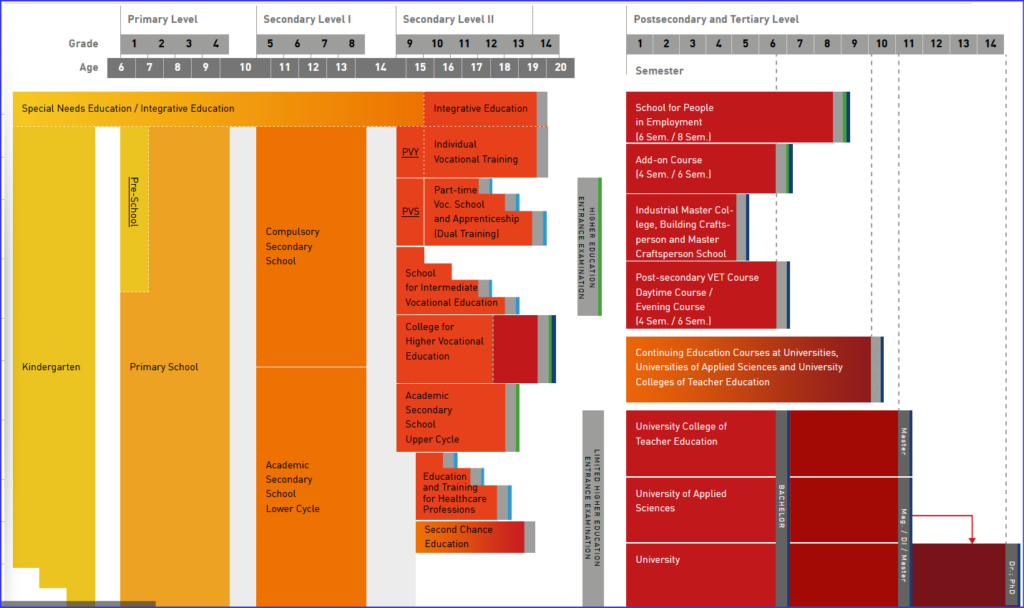
The education systems of different countries are organised differently and are therefore often difficult to compare with each other. ISCED is a statistical tool used for the international comparison of educational qualifications. ISCED helps educational research and education policy to compare, analyse and improve the education systems in the OECD area(www.oecd.org), which currently has 34 member states.
By citing the ISCED level from kindergarten to university, experts in other countries can recognise more quickly and better what level of education a course of education leads to.
ISCED 2011 takes into account current developments and significant changes in education systems worldwide since the last revision of ISCED in 1997. For Austria, ISCED 2011 brings a far-reaching change in the presentation of upper secondary vocational schools (BHS). According to the new criteria, the 4th and 5th year of BHS now correspond to level 5; this is referred to as ‘Short Cycle Tertiary Education’. This means that competences acquired at a BHS can be directly compared with academic programmes (e.g. a short cycle degree in the UK), which will facilitate permeability and mobility. Furthermore, the tertiary sector of the education system has been adapted to current developments and is now divided into 3 levels.
In contrast to its predecessor programme ISCED 97, ISCED 2011 offers more precise differentiation options between the educational levels:
Level 0 – Elementary
In addition to formal early childhood education for children from the age of three until they start school, this level now also includes early childhood education for children up to the age of three.
Level 1 – Primary education
In the Austrian education system, this level comprises primary school.
Level 2 – lower secondary level
This level comprises the first 4 years of secondary school and the lower level of the Allgemeinbildende höhere Schule (AHS).
Level 3 – Secondary level II
This level includes educational institutions that are dedicated to general education or vocational training after lower secondary level. This area includes individual vocational training (in accordance with § 8b BAG) polytechnic schools, vocational schools & apprenticeships, intermediate vocational schools, upper secondary vocational schools up to the 3rd year, the upper level of upper secondary general schools and training programmes for healthcare professions.
Level 4 – Post-secondary, non-tertiary education
The 4th level of the ISCED classification includes qualifications that are categorised as secondary education but do not yet fall into the tertiary sector. These programmes include, for example, health and nursing schools as well as some courses at universities or universities of applied sciences.
Level 5 – Short tertiary education programme
Level 5 of the ISCED classification is designed for all post-secondary qualifications that provide graduates with professional knowledge, skills and competences that are typically practice-oriented. A special characteristic is the occupation-specific orientation. Level 5 includes higher vocational schools from the 4th year onwards, postgraduate courses, schools for professionals, foreman, building tradesman and master craftsman schools as well as colleges.
Such programmes can also be defined as the first part of a Bachelor’s programme.
Level 6 – Bachelor’s or equivalent education programme
Level 6 of the ISCED classification includes Bachelor’s degree programmes at universities, universities of applied sciences and teacher training colleges. Equivalent educational programmes in other fields also fall into this category.
Level 7 – Master’s or equivalent educational programme
The 7th level of the ISCED classification includes Master’s degree programmes at universities, universities of applied sciences and university colleges of teacher education. Equivalent educational programmes in other fields also fall into this category.
Level 8 – Doctorate or equivalent educational programme
The 8th level of the ISCED classification comprises the highest forms of higher education, the doctorate and the habilitation. (Dr, PhD)
We will adapt the African school system so that it is more comparable with the ISCED classification in future. With ACAPMUSSC-MYC, we want to ensure that African tradespeople from vocational schools in Africa and graduates of African universities are also recognised in the EU and in Europe in the future. There is still a long and instructive road ahead of us. The aim is for the AU (African Union) and the EU (European Union) to draw up and sign a joint knowledge treaty.
The EU currently has 27 member states and the AU 55 member states. Together, these 2 unions would form the largest economic area in the world. The NADEUM’s GOAL is to follow this path peacefully and for the benefit of all.
UNESCO:
OECD > eurostat
Diagram showing the „Austrian education system„:
Wissenswertes kundgetan, Aktualisierung am: 2024-10-02 ; Erstellt am 2024-07-22 Übersetzungen oder Lectorate mit Hilfe von DeepL.com & Write verfasst. <> Translations or lectorates written with the help of DeepL.com & Write.